FS show all show all steps. Which sampling method does not require a frame.
 Management Accounting For Exams From February Ppt Download
Management Accounting For Exams From February Ppt Download
You must be signed in to discuss.
What sampling method does not require a frame. Systematic sampling doesnt require a frame. Other Effective Sampling Methods Discussion. Which sampling method does not require a frame.
Which sampling method does not require a frame. Which sampling method does not require a frame. Attribute Sampling In attribute sampling data is in the attribute form and the result either conforms or does not conform.
In most situations the output of a survey conducted with a non-probable sample leads to skewed results which may not represent the desired target population. Chapter Problem is solved. The sampling frame not only defines the population to which the finding from your sample can be inferred but it also the.
FS show all show all steps. 100 7 ratings for this solution. Simple random O D.
Which sampling method does not require a frame. The sampling frame must be representative of the population and this is a question outside the scope of statistical theory demanding the judgment of experts in the particular subject matter being studied. All the above frames omit some people who will vote at the next election and contain some people who will not.
The logic of random selection requires a rigorous sampling frame. What is the basic requirem 0212. If these adults are different in some way from those who own a cell phone on our survey outcomes then selection bias may result.
We have solutions for your book. Simple random c. Answer to Which sampling method does not require a frame.
Choose the correct answer below. View a full sample. You may have no better option for a sampling frame or the frame may have been decided by someone else.
In this particular case its called coverage bias. Some residents may have moved since the most recent census. View a sample solution.
For example say a researcher is. What is a sampling. 100 7 ratings for this solution.
FS show all show all steps. All of the above sampling methods require a frame. Which sampling method does not require a frame.
In the example above the sample only requires a block-level city map for initial selections and then a household-level map of the 100 selected blocks rather than a household-level. All of the above sampling methods require a frame. We have solutions for your book.
Likewise adults with only a land line telephone or no telephone at all will be not be covered by this sampling frame. QUESTIONWhich sampling method does not require a frameANSWERA Simple randomB StratifiedC ClusterD SystematicE All of the above sampling methods re. Ideally our sampling frame would contain all 100000 such residents so that we could obtain a sample that is representative of the target population.
View a sample solution. Chapter Problem is solved. FS show all show all steps.
It also means that one does not need a sampling frame listing all elements in the target population. Systematic sampling does not require a well-defined sampling frame. Some frames will contain multiple records for the same person.
Get the detailed answer. People not in the frame have no. View a full sample.
Which sampling method does not require a frame. However in reality our sampling frame usually doesnt match our target population perfectly for a list of reasons including. Which sampling method does not require a frame.
All of the above sampling methods require a a. But there are situations such as the. The process of using chance to select individuals from a population to be included in the sample stratified sample separating the population into nonoverlapping groups called strata and then obtains a simple random sample from each stratum.
Fundamentals of Statistics 5th. Instead clusters can be chosen from a cluster-level frame with an element-level frame created only for the selected clusters. Name the four basic sampli 0245.
All of the above sampling methods require a frame. The non-probability method is a sampling method that involves a collection of feedback based on a researcher or statisticians sample selection capabilities and not on a fixed selection process.
Purposive sampling is different from convenience sampling and is also known as judgmental selective or subjective sampling. Convenience Sampling and Purposive Sampling are Nonprobability Sampling Techniques that a researcher uses to choose a sample of subjectsunits from a population.
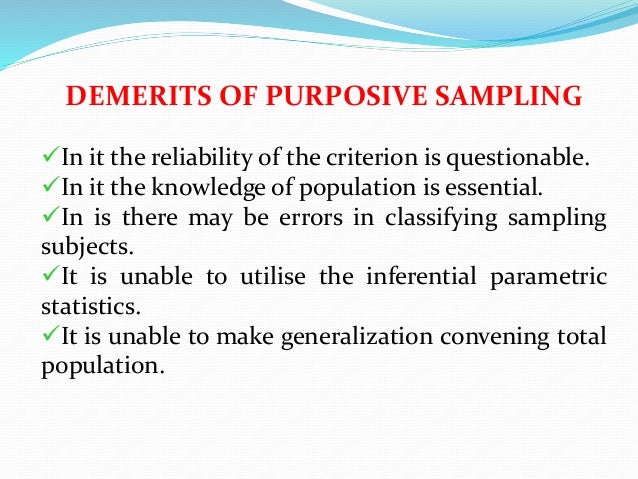 Non Probability Sampling Convenience Purposive
Non Probability Sampling Convenience Purposive
One Final Consideration on the Advantages and Disadvantages of Purposive Sampling.
Purposive convenience sampling. Purposive sampling also known as judgment selective or subjective sampling is a sampling technique in which researcher relies on his or her own judgment when choosing members of population to participate in the study. Most research is conducted on convenience and purposive samples that may be randomly or nonrandomly drawn. Purposive sampling relies on the presence of relevant individuals within a population group to provide useful data.
Convenience sampling is a method of collecting samples by taking samples that are conveniently located around a location or Internet service. Die Fallauswertung erfolgt dann bei grober Kenntnis der Daten aus der Minimax-Kontrastierung dh. Die Fälle werden bei der.
Internes Theoretisches Sampling Aufgrund verdeckter Merkmale des Falles die nicht vorab erst in der Fallbearbeitung selbst erkennbar werden wird eine convenience Stichprobe untersucht. A purposive sample is the one whose characteristics are defined for a purpose that is relevant to the study. QUALITATIVE SAMPLING TECHNIQUES CONVENIENCE PURPOSIVE.
Purposive and convenience sampling are both a form of sampling typically applied for qualitative data collection. We have all seen studies that leverage students in the computer science classes. Convenience sampling would involve selecting whomever is willing to participate - regardless of qualifications knowledge or experien.
Convenience sampling is a non-probability sampling technique where samples are selected from the population only because they are conveniently available to researcher. A purposive sample is a non-probability sample that is selected based on characteristics of a population and the objective of the study. A convenience sample is the one that is drawn from a source that is conveniently accessible to the researcher.
Convenience sampling and purposive sampling are two different sampling methods. Convenience sampling is when researchers leverage individuals that can be identified and approached with as little effort as possible. Convenience sampling is the most common form of nonprobabilistic sampling mostly because it is misused.
Purposive sampling is a non-probability sampling method and it occurs when elements selected for the sample. The terms purposive sampling and convenience sampling are often used interchangeably but they do not mean the same thing. NON PROBABILITY SAMPLING CONVENIENCE PURPOSIVE.
Convenience Sampling and Purposive Sampling are Nonprobability Sampling Techniques that a researcher uses to choose a sample of subjectsunits from a population. Both convenience and purposive sampling are forms of nonprobability sampling - versus probability random sampling as is typically applied for quantitative research. Although Nonprobability sampling has a lot of limitations due to the subjective nature in choosing the sample and thus it is not good representative of the population but it is useful especially when randomization is impossible like.
Whereas convenience sampling involves asking people who happen to be convenient to the researcher on the street or using friends and family those using a purposive sample will endeavor to direct their survey at a range of respondents who are ultimately representative of at least the extremes of variables under consideration. Convenience Sampling and Purposive Sampling are Nonprobability Sampling Techniques that a researcher uses to choose a sample of subjectsunits from a population. These samples are selected only because they are easy to recruit and researcher did not consider selecting sample that represents the entire population.
Convenience sampling does not distinguish characteristics among the participants. Whereas purposive sampling focuses on the selection of participants possessing characteristics associated with the research study. Although there are several different purposeful sampling strategies criterion sampling appears to be.
The goal of this work is to find a range of cases that meet. This article first explains sampling terms such as target population accessible population simple random sampling intended sample actual sample and statistical power analysis. Sampling is the act process or technique of selecting a representative part of a population for the purpose of determining parameters or characteristics of the whole population.
These are often individuals that are geographically close to the. If researchers cannot find enough people or units that meet their criteria then this process will become a waste of time and resources. QUALITATIVE SAMPLING TECHNIQUES CONVENIENCE PURPOSIVE SNOWBALL QUOTA - YouTube.
Purposeful sampling is widely used in qualitative research for the identification and selection of information-rich cases related to the phenomenon of interest. These terms are then used to explain the difference between convenience sampling and purposive sampling Convenience sampling is a non-probabilistic sampling. Purposive Sampling vs.
Non-probability sampling is a non-random and subjective method of sampling where the selection of the population elements comprising the sample depends on the personal judgment or the discretion of the sampler. Non-probability sampling is defined as a sampling technique in which the researcher selects samples based on the subjective judgment of the researcher rather than random selection.
Https Medcraveonline Com Bbij Bbij 05 00148 Pdf
Realizing that a probability statistical technique cannot be used to calculate sample size.
Non probability purposive sampling technique. Purposive sampling may also be used with both qualitative and quantitative re- search techniques. Non-Probability Sampling Technique Non-probability technique is one of the sampling technique which helps researcher to create sample from a population of interest target population for a particular study. Non-probability sampling represents a group of sampling techniques that help researchers to select units from a population that they are interested in studying.
Non-probability sampling Unequal chance of being included in the sample non-random Non random or non - probability sampling refers to the sampling process in which the samples are selected for a specific purpose with a pre-determined basis of selection. Purposive sampling is a popular method used by researchers due to the fact that it is extremely time and cost effective when compared to other sampling methods. Purposive sampling provides non-probability samples which receive selection based on the characteristics which are present within a specific population group and the overall study.
It is a less stringent method. Purposive sampling is different from convenience sampling and is also known as judgmental selective or subjective sampling. Non-probability sampling is defined as a sampling technique in which the researcher selects samples based on the subjective judgment of the researcher rather than random selection.
It is carried out by observation and researchers use it widely qualitative research. Further the numerous technique options outlined above make purposive sampling a versatile research method that can be tailored to enhance a studys effectiveness. It is a process that is sometimes referred to as selective subjective or judgmental sampling but the actual structure involved remains the same.
It is not statistically justified to use. The purposive sampling technique is a type of non-probability sampling that is most effective when one needs to study a certain cultural domain with knowledgeable experts within. Purposive sampling is a non-probability sampling method and it occurs when elements selected for the sample are chosen by the judgment of the researcher.
I will use a nonprobability purposive sampling technique. In non-probability sampling technique the participants do not get equal chances of being selected. NON PROBABILITY SAMPLING CONVENIENCE PURPOSIVE.
The basics to learn more about terms such as unit sample and population. Purposive sampling is a non-probability sampling method and it occurs when elements selected for the sample are chosen by the judgment of the researcher. Collectively these units form the sample that the researcher studies see our article Sampling.
The distinguishing feature of non-probability sampling is that in such sampling the selection of population elements is not made through any probability mechanism and. Sampling is the act process or technique of selecting a representative part of a population for the purpose of determining parameters or characteristics of the whole population. Under this technique as such there is no probability attached to the unit of the population and the selection relies on the subjective judgment of the researcher.
An Overview of the Method and Its Applications. A purposive sample is a non-probability sample that is selected based on characteristics of a population and the objective of the study. The sample is not a proportion of the population and there is no system in selecting the sample.
Purposive sampling Purposive sampling also known as judgment selective or subjective sampling is a sampling technique in which researcher relies on his or her own judgment when choosing members of population to participate in the study. Purposive sampling also known as judgment selective or subjective sampling is a sampling technique in which researcher relies on his or her own judgment when choosing members of population to participate in the study. This sampling method depends heavily on the expertise of the researchers.
When in a sampling method all the individuals of the universe are not given an equal opportunity of becoming a part of the sample the method is said to be Non-probability sampling. Non Probability Sampling Convenience Purposive.
Example of sampling bias in a simple random sample You want to study procrastination and social anxiety levels in undergraduate students at your university using a simple random sample. Use a random number generator to select the sample using your sampling frame population size from Step 2 and your sample size from Step 3.
In improving the sampling design supplementary information for the field covered by the sampling frame may also be valuable.
Sampling frame example. Using simple examples this video tries to clarify the difference between Sample Sampling Unit and Sampling Framesamplingframe samplingunit sample. Sampling Frame and Sampling Unit List of household and persons enumerated in population census. For instance using the above example the sampling frame doesnt include teenagers who access the web from their mobile phone who arent at home at the time of the call or who simply arent interested in participating in surveys.
Some numbers listed in the phone book are no longer working numbers because the people in the household that had the number have moved out of the city. Examples of a sampling frame include the telephone book an association directory listing the firms in an industry a mailing list purchased from a commercial organization a. For example it will be extremely challenging to survey shelterless people or illegal immigrants.
In research these units make up the. Consider for example a survey aimed at establishing the number of potential customers for a new service in the population of New York City. Accuracy is defined as the degree to which bias is absent from the sample.
For example if your sample size is 100 and your population is 500 generate 100 random numbers between 1 and 500. The sample should be the best representative of the population under study. In the ideal case the sampling frame should coincide with the population of interest.
You assign a number to every student in the research participant database from 1 to 1500 and use a random number generator to select 120 numbers. For an easy example of these types of frame errors consider sampling households within a city using the telephone white pages as the sampling frame. In such cases using the snowball theory researchers can track a few categories to interview and derive results.
About which inferences and estimates are desired. Now put Sampling Units into their proper context and you have the Sample Frame which consists of a listing of all possible Sampling Units. Sample frame survey frame is the actual set of units from which a sample has been drawn.
Units could be people organizations or existing documents. In these circumstances it is possible to easily identify all members of the target population and ensure that they have a positive probability of being sampled. In some cases the population and sampling frame are known with certainty.
In the case of a simple random sample all units from the sampling frame have an equal chance to be drawn and to occur in the sample. Sampling frame synonyms. These are erroneous inclusions.
Snowball sampling is a sampling method that researchers apply when the subjects are difficult to trace. Sampling Frame Practical Approach for Determining the Sample Frame Expected When developing a research study one of the first things that you need to do is clarify all of the units also referred to as cases that you are interested in studying. Examples of these types of situations usually involve smaller populations like groups with known e-mail addresses visitors to particular Web-sites or the like.
An accurate unbiased sample is one that exactly represents. Some households choose to have their phone numbers unlisted. The sampling frame is the information that locates and defines the dimensions of the universe.
Researchers also implement this sampling method in situations where the topic is. The target population provides the overall context and represents the collection of people housing units schools etc. A good sample should satisfy the below conditions-Representativeness.
Even getting into the sampling frame doesnt ensure that the person becomes a part of the final sample group. Simple random sampling in research. A sampling frame is a list of the actual cases from which sample will be drawn.
A map of areas of a country showing the boundaries of area units.
Samples are drawn from subgroups at regular intervals. Complex sampling techniques are used only in the presence of large experimental data sets.
 Sampling Methods Simply Psychology
Sampling Methods Simply Psychology
Values obtained from study of a sample.
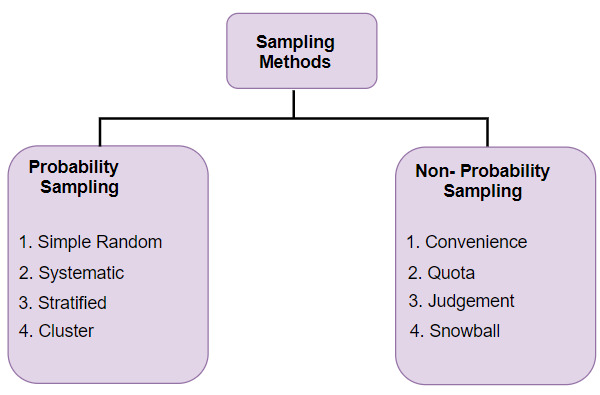
What are the different sampling techniques in statistics. Optimum allocation stratified sampling. Following are the types of probability sampling methods. The process of learning about population on the basis of sample drawn from it.
Rational subgrouping is a sampling technique whose main aim is to produce data for control charts. The sampling techniques simple cluster stratified and systematic are all probability sampling techniques and involve randomization. Observational Math Statistics and probability.
This sampling method is as easy as assigning numbers to. Three elements in process of sampling. One of the best probability sampling techniques that helps in saving time and resources is the.
Outcome of sampling might be biased and makes difficult for all the elements of population to be part of the sample equally. Here the samples are selected based on the availability. What are the types of probability sampling.
- This method refers to a method having following properties. In simple words probability sampling also known as random sampling or chance sampling utilizes random sampling techniques and principles to create a sample. Types of studies experimental vs.
There are several different sampling techniques available and they can be subdivided into two groups- 1. Disproportionate sampling means that the size of the sample in each unit is not proportionate to the size of the unit but depends upon considerations involving personal judgement and convenience. There are two basic types of sampling methods.
This is the currently selected item. Sampling is a method used in statistical analysis in which a decided number of considerations are taken from a comprehensive population or a sample survey. In this video we discuss the different types of sampling techinques in statistics random samples stratified samples cluster samples and systematic sample.
Probability sampling methods ensures that the sample choosen represent the population correctly and the survey conducted will be statistically valid. Simple random sampling as the name suggests is an entirely random method of selecting the sample. When efficiency is required.
The methodology used to sample from an extensive population depends on the type of study being conducted but may involve simple random sampling or systematic sampling. The population have N objects. Cluster sampling is a method where the researchers divide the.
This method of sampling is. Such values from study of population. Probability sampling uses statistical theory to randomly select a small group of people sample from an existing large population and then predict that all their responses will match the overall population.
There are four types of probability sampling techniques. However convenience sampling is a non-probability or non-random sampling technique as it relies on the researchers ability to select the sample. Random sampling systematic sampling stratified sampling fall into the category of simple sampling techniques.
What is probability sampling. This type of sampling is also known as non-random sampling. In fact systematic sampling is one of the most popular methods used for process sampling.
Techniques for random sampling and avoiding bias. Probability sampling involves random selection allowing you to make statistical inferences about the whole group. Selecting the sample Collecting the information Making inference about population Statistics.
And while making precise estimates about relatively small groups within large populations Salant p59. There are four types of probability sampling techniques.